Start of instrument development activities:
Absolut System designed a custom thermal braid and supplied 2 LPT6510 cryocoolers.
Image: Airbus courtesy
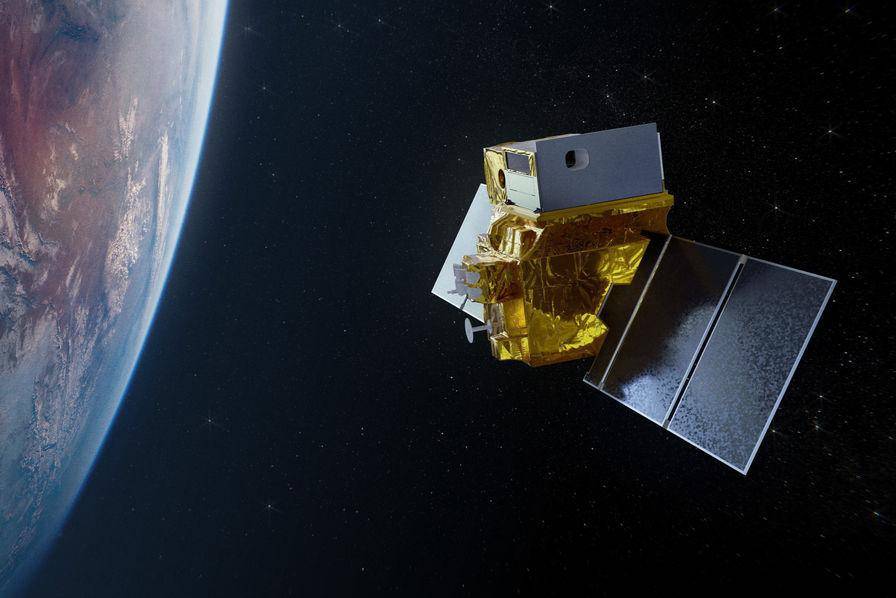

The result of a Franco-Indian partnership, the TRISHNA project collects thermal infrared images of the Earth’s surface with unrivalled resolution and revisit frequency.
In recent years, global warming has intensified considerably, leading to a number of global and localized changes. Rising sea levels and ocean temperatures, intensified precipitation and storms (rain and hail), increased drought, retreating Arctic sea ice and snow cover are all to be expected if temperatures rise above 4°C by 2100.
As temperature is an indicator of the energy balance of land surfaces of all kinds, its study allows us to see the evolution and obtain a zoning (mapping) in order to find localized and adapted solutions.
The project collects thermal infrared images of the earth’s surface. In this spectral range (4μm to 15μm), radiation depends on the emissivity properties of surfaces, i.e. their ability to reflect heat. Satellite sensors measure the apparent temperature of objects.

Absolut System designed a custom thermal braid and supplied 2 LPT6510 cryocoolers.
Image: Airbus courtesy


During the exploration phase, the satellite flies over the same point every eight days, from the same angle.

Absolut System designed a custom thermal braid and supplied 2 LPT6510 cryocoolers.
Image: Airbus courtesy


During the exploration phase, the satellite flies over the same point every eight days, from the same angle.

Absolut System designed a custom thermal braid and supplied 2 LPT6510 cryocoolers.
Image: Airbus courtesy


During the exploration phase, the satellite flies over the same point every eight days, from the same angle.
Developed by CNES, this telescope contains 4 thermal infrared cameras, measuring the Earth’s surface temperatures. The IRT instrument is based on a scanner concept (swath +/-34°) and a scanning mechanism that continuously rotates the entrance plane mirror, so that the telescope’s optical field of view scans the entire swath over what is known as a basic repetition cycle.
Absolut System provides 60K cryogenic cooling for the detector and filters, using two LPT6510 cryocoolers in hot redundancy via a cold thermal link (custom thermal braid). This cold optical assembly is thermally isolated from the rest of the instrument by a cryostat using additive layer manufacturing (ALM) technology, perfectly mastered by our engineers.
Developed by ISRO, this 6-camera instrument in the visible/SWIR range can be used to identify crop type and condition. This project was made possible thanks to Absolut System’s cryogenic expertise, based on the IASI and METIMAGE experiments, two flagship projects for which our teams supplied thermal braids currently in flight. For this instrument, Absolut System is supplying a thermal link (TLA) integrated into the cryostat.
It will be possible to monitor the evolution of water stress in plant cover around the globe.
This project will enable us to take stock of marine ecosystems: level of fishery resources, quality of seawater and continental waters, monitoring of rivers and lakes.
In the urban environment, neighborhood development and human activities generate microclimates that can affect the quality of life and health of city dwellers. TRISHNA’s measurements will enable us to understand the effect of revegetation and help us to make the right choices when it comes to building.
At high latitudes and altitudes, access to surface temperatures will improve understanding of climate change on snow, polar caps, glaciers and permafrost. In the high mountains, monitoring the water cycle via glaciers, snow and lakes offers the possibility of better management of the basins they feed.
Le bilan énergétique des nuages est un poste clé du bilan radiatif global de la Terre. À ce titre, les mesures thermiques de TRISHNA contribueront à affiner nos connaissances sur le changement climatique en cours.